Filters

4 Color
CMYK printing uses the four process color inks—cyan, magenta, yellow and black—to reproduce a broad spectrum of colors and tones and is made possible by repeating the halftone process for each color.

6 Color
CMYK printing with the addition of two spot colors to create an even larger color gamut (also known as Hexachrome printing).

Aqueous Coatings
Water-based aqueous coating can be applied over wet ink from a special coater tower. Aqueous seals a press sheet instantly allowing the ink to continue to dry underneath. Matte, dull and lay flat aqueous are recommended for uncoated paper. Aqueous coatings generally cover the entire sheet because they do not yellow over time. Like varnish, aqueous coating primarily prevents rub off.

Aqueous Inks
Water-based inks, usually described as pigment or dye, which requires media treated with a inkjet-receptive coating.

Aqueous Single-Pass Inkjet Inks
Water-based inkjet inks where the colorants can be pigment or dye. Designed for high-speed inkjet printers utilizing “waterfall” technology print heads.

Case Bound
Book pages are either perfect bound or sewn together first, then placed into a case consisting of board covered with paper, cloth or another substrate.

Comb Binding
Rectangular holes are punched into the binding edge, then placed into the teeth of an open plastic binding comb and closed to secure the sheets.

Die Cutting
The cutting of paper into decorative shapes or patterns using a steel cutting die.

Digital Printing
Printing imaged by digital data from prepress systems using liquid ink or powdered toner.

Dry Toner
Dry toner is fine powder made of pigments embedded inside supersmall polymer beads. These beads melt to the surface of the printing substrate during the fusing phase of the printing process.

Duotone
Two color halftones that use two screens at different angles and two colors of ink on different plates to create more depth and contrast.

Dye Sublimation Direct Inkjet Inks
A process using high-energy disperse inks which are printed directly onto polyester fabric and then typically cured through an in-printer heat press.

Dye Sublimation Transfer Inkjet Inks
A process using low-energy disperse inks which are typically printed onto a specially treated paper and then transferred to the polyester fabric through the use of (separate) heat press.

Eco-Solvent Inkjet Inks
Refined mineral oil-based inks where the pigment colorants are evaporated and penetrate into the surface of the substrate via in-printer heat.

Edge Painting
The painted edge of a book. Historically, bookbinders would gild the edges of books with gold to show their importance. Today edge painting is typically done with opaque inks (sometimes metallic inks), resulting in a colorful edge surface. Foil Edging is done with metallic foil (such as gold or silver), resulting is a smooth, reflective surface.
Also known as Edging.

Embossing/Debossing
Embossing is impressing an image in relief to achieve a raised surface. Debossing is pressing an image into paper so it lies beneath the surface. Both can be registered over printing or on blank paper which is called blind embossing/debossing.

Engraving
Metal plates are etched with a recessed image of the design, and coated with opaque ink. The plate is blotted leaving only the image with ink. Once paper is fed into the printer, intense pressure is applied, creating raised type and graphics.

Fluorescent Inks
Semi-transparent and naturally bright, fluorescent inks increase the clarity and brightness of images printed on uncoated paper. Fluorescent inks may be used as spot colors or may be added to process colors to alter a color image.
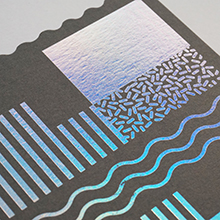
Foil Stamping
Foil film comes in a variety of colors, finishes and effects. A metal die is created for each foil color used in the design. The die is heated and then stamped using pressure, sealing a thin layer of the foil to the paper.

Half Tone
The reproduction of continuous-tone images, through a screening process, which converts an image into dots of various sizes and spacing. The size and angle of the screen controls the size and proximity of the dots to create the desired shade.

Hand Sewn
Sheets are hand sewn with needle and thread in various patterns.

Hexachrome
Six-color process printing, adding green and orange inks to the traditional cyan, magenta, yellow and black. The added colors make a broader gamut of color reproduction possible. Hexachrome inks are brighter, cleaner and more vibrant than CMYK, but can carry higher ink and press costs.

i-Tone
Mohawk’s proprietary Digital with i-Tone surface has a unique affinity for both liquid and dry toners, offering breakthrough performance on HP Indigo presses and color digital production presses using dry toner. Mohawk’s i-Tone papers have exceptional transfer, adhesion and image durability on smooth and textured papers.

Inkjet
Inkjet inks are made up of pigments dissolved and dispersed in liquid. The resulting colored ink is “jetted” (thus the name) in small drops to the surface of the substrate chosen as your print surface.

Inxwell
A revolutionary and exclusive technology, created and patented by Mohawk, that produces text and cover papers with an uncoated feel, but with the added advantages of superior ink holdout, lower dot gain and significantly increased opacity.

Latex Inkjet Inks
Water-based inks where latex polymers and pigment particles are bonded to the surface of the substrate with in-printer heat.

Lay Flat
A variation of traditional perfect binding where the spine of the cover is not attached to the book block, allowing the book to lay flat when open, and images are not lost in the gutter.

Letterpress
A technique of relief printing using a printing press. A surface with raised letters is inked and pressed to the surface of the printing substrate to reproduce an image in reverse.

Liquid Toner
Liquid toner uses pigments in polymer beads, dispersed in an oil that gives them the consistency of traditional printing inks. This oil evaporates during the heat-driven fusing process.

Loop Stitched
Similar to saddle stitching, but the wire is formed into a circular loop sticking out beyond the spine, designed to be inserted onto a ring binder.

Match Colors
A specified premixed ink color which has been mixed according to a formula. Match colors are more accurate than process colors which use screens and can vary from one print run to the next. Also referred to as a spot color or Pantone® Matching System (PMS).

Metallic Inks
Metallic powders in a varnish base create images with metallic luster. Leafing inks which have metal flakes that rise to the top of the ink mixture have more shine, but increased rub off. The metal flakes in non-leafing metallic inks sink down with less rub off and a little less shine. Non-leafing inks with a dull varnish or aqueous coating perform most reliably on uncoated paper.

Offset Printing
A commonly used printing technique in which the inked image is transferred from a plate to a rubber blanket, then to the printing surface. When used in combination with the lithographic process, which is based on the repulsion of oil and water, the offset technique employs a flat (planographic) image carrier on which the image to be printed obtains ink from ink rollers, while the non-printing area attracts a water-based film (called "fountain solution"), keeping the non-printing areas ink-free.

Packaging
Papers and folding boards available to help brands make an impact in the retail environment. Applications include boxes, bags, hang tags, etc.

Perfect Bound
The spine of the book block is cut and roughened, adhesive is applied to the rough edge, before a paper cover is wrapped around and glued in place.

Risograph (RISO)
Originally invented to make use of low cost inks, Risograph is an intermediate between digital printing and screen printing that comes with inherent quirks: off-registration, limited colors, uneven ink performance — in short: an inaccurate and inconsistent process. Much like the Holga camera with its brilliant simplicity, lack of precision and light leaks, Risograph’s bugs are its features. Risograph’s results are reminiscent of handmade screen-prints, coveted for their effective adoption of very bold, bright and vibrant colors.

Saddle Stitching
Folded signatures are nested, placed over a "saddle" and stapled together through the center fold with wire staples.

Screw Bound (Chicago Screw)
Holes are drilled into the pages and cover of a book block, and aluminum screw posts are tightened to hold the pages together.

Side Stiching
Folded signatures or cut sheets stapled along the side of the spine of the book from front to back.

Silk Screen
Process of printing by hand. A mesh cloth is stretched over a wooden frame. The design or image is painted on this screen and is squeegeed through onto the printing surface.

Singer Sewn
Pages are sewn together with the help of a Singer sewing machine, through the spine or on the side of a book, similar to side stitching.

Smyth Sewn
A method of sewing together folded, gathered and collated signatures with thread through the folds of the individual signatures.

Spiral Binding
Sheets held together by continuous coil of wire or plastic looped through a series of holes punched alongside the binding edge.

Tape Bound
Sheets are bound together with an external strip of book tape or cloth. For additional strength, side stitching or glue is often used to hold the pages together before the tape is applied.

Thermography
A post print process of creating raised areas of print or images on paper. Resinous powder is applied to the wet surface of the ink and fused by heat, or infrared radiation.

Touchplates
Touchplates or bump plates use one unit of the press to apply extra ink to certain areas of an image that require an extra pop. Photoshop or other software is used to isolate touchplate areas and incorporate them into an image.

Ultraviolet (UV) Coating
Like UV inks, UV coating is dried quickly with UV radiation. Applied by silkscreen, UV coatings deliver the best rub protection and fastest drying time. UV coating can be used on smooth, cover-weight papers. Pre-testing is recommended. UV coasting is usually specified in gloss, although matte, dull and satin UV coatings are available. Options include spot and overall coverage.

Ultraviolet (UV) Printing
UV inks produce sharp images because they are cured instantly under UV lights on press. UV printing minimizes dot gain and also eliminates the need for varnish or aqueous coating.

UV-Cured Inkjet Inks
An ink generally composed of synthetic resins and colored pigments that is instantly cured by in-printer UV lamps or LEDs which encapsulates/seals the ink to the surface of the substrate.

Varnish Coatings
A petroleum-based sealant applied by a standard inking unit on press. It can be specified in matte, dull, satin or gloss and applied to the entire sheet or only in selected areas. Matte and dull varnishes are recommended for uncoated papers. (Gloss and satin varnishes can make images appear uneven or mottled.) Varnish darkens inks on uncoated paper—making solid blacks blacker‚ but will not provide any other visual effect.

Web Printing
A form of offset printing using a continuous roll of paper which is then fed through the printing press. Pages then cut to size after printing. Web offset printing traditionally is used for high-volume publications such as magazines, newspapers, catalogs and brochures.

White Ink
Opaque white ink can create a unique print effect — it is a non-transparent ink which does not let any of the base color show though. The more hits of white used, the more it stands out from the background. White ink can be used alone, or as the base to print color on top, which allows full color imagery to be printed on dark colored paper.

Wide Format
Process of printing on large format paper and rolls, which can range from two to more than 15 feet in width — typically using inkjet printing technology.

Wire Binding
Individual sheets are stacked together and holes are punched along the binding edge. A “C” shaped wire is pushed into the holes and pinched together to create a circle.





























